
The killall command does essentially the same, with the main difference being that it lets you specify target processes by their names.

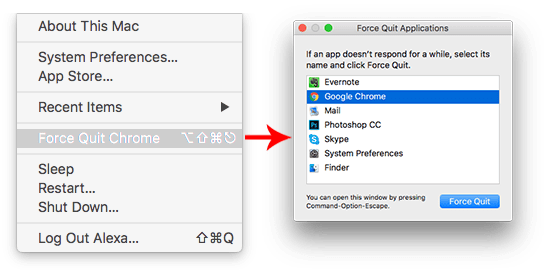
With kill you have to specify the target process by its process ID. do some cleaning up before terminating.Ī more forceful signal would be the KILL (9) signal, which forces the process to terminate immediately.įor more information and a complete list of signals, run man kill. The specification of the TERM signal is designed to give the addressed process a chance to shutdown gracefully, i. If you don't specify a signal, the default will be used, which is the TERM (15) signal. The signals have defined names and numeric codes. There are many different signals that can be sent to processes. If you have any further questions, just leave your comment below.The kill command is a UNIX command (macOS is a UNIX variant) that sends signals to processes. I hope this article will help you to learn more about how to force quit Mac apps with shortcuts, as well as terminal commands. For example: kill -9, to force quit Finder. For example: killall Finder, to force quit Finder. If you don’t like to use methods that are mentioned above (even though these ways are simpler), then open Terminal app (under Applications -> Utilities -> Terminal), and use any of two commands below: Six Ways to Quit an App in Any Version of macOS Use a keyboard shortcut: hit Command + Option + Escape to bring up the Force Quit Applications window, and. To force quit any programs on your Mac computer, open Activity Monitor (also known as Task Manager Mac), select the program you want to close and click on the “ Force Quit” button. For example: Force Quit Finder.įorce Quit Mac Apps With Activity Monitor In order to force quit a program from Apple menu, press and hold Shift key on your keyboard, and then click on the Apple logo > Force Quit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
